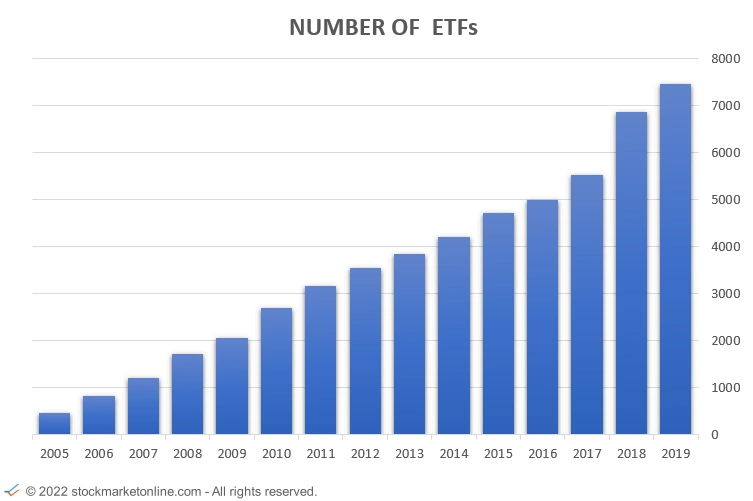
Investing – What is an ETF?
ETFs are particularly good investment vehicles, for investing in different indices or themes.
What is an ETF - Exchange Traded Fund?
An ETF is a passively managed fund. This means that various investment objects are combined in an ETF.
Properties of ETFs?
-
ETFs are mostly passively managed. Passive means that a computer program does most of the work. Due to the passive management ETF are very cheap investment objects and generate very few costs.
-
Like stocks, ETFs can be traded during normal trading hours.
-
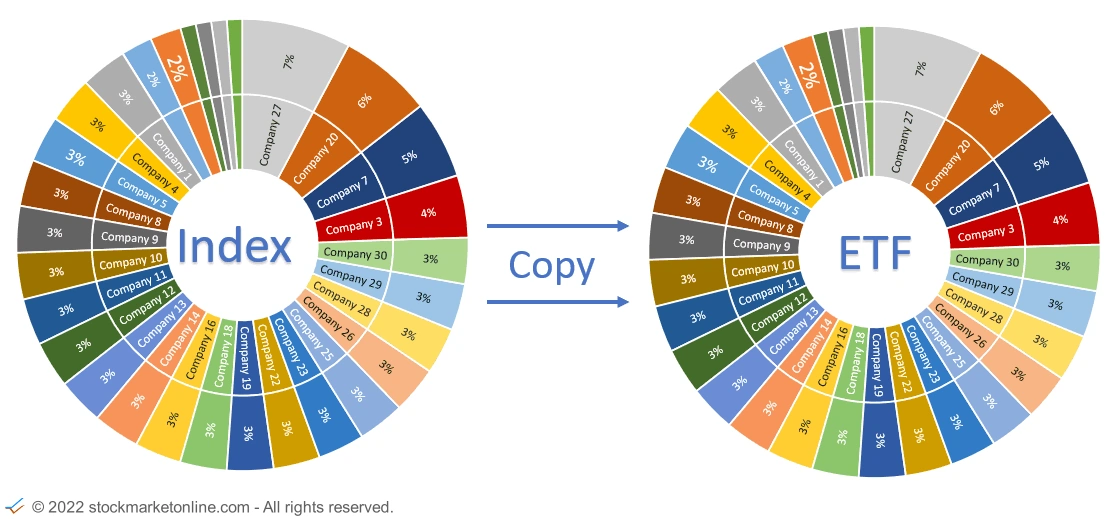
Most ETFs track an index. The major stock indices, sectors, currencies and commodities are used.
There are also ETFs that do not track an index 1 to 1 but have extra rules for the composition of the companies in the ETF.
A good differentiation example is the ETF 'SPY' on the S & P500 index (which replicates the index 1 to 1) and the 'RSP' ETF, which replicates the SP500 index modified. The same companies are in the 'RSP' ETF as in the SP500. But in contrast to the 'SPY', in the 'RSP' all companies are weighted equally. In the SPY, the companies are weighted equally as in the SP500.
-
ETFs also replicate subject areas that are not available as an index.
-
ETFs also replicate subject areas that are not available as an index. For example, ETFs with ESG criteria or ETFs that track individual megatrends.
Why ETFs
ETFs are becoming increasingly popular due to their flexible design.
ETF advantages
-
ETFs are tradable like shares.
-
ETFs are diversified because they track the performance of multiple companies.
.. More .. Diversifications -
ETFs are protected from the issuer's bankruptcy risk. If an issuer goes bankrupt, the ETFs are protected from this risk.
-
ETFs are very favorable instrument to build a diversified portfolio.